The Employee Provident Fund (EPF) is a mandatory savings scheme for employees in India, established under the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. It aims to provide financial security to employees after retirement and is managed by the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
Key Features of EPF
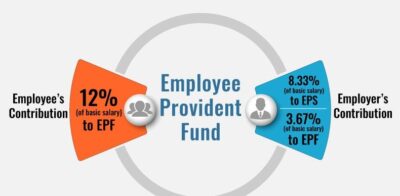
- Contributions:
- Both the employer and the employee contribute 12% of the employee’s basic salary and dearness allowance (if any) to the EPF.
- Employers also contribute an additional 8.33% towards the Employee Pension Scheme (EPS) for employees earning up to ₹15,000.
- Interest Rate:
- The EPF accumulates interest, which is declared annually by the EPFO. The interest earned is tax-free.
- Withdrawal:
- Employees can withdraw their EPF balance upon retirement, resignation, or under certain conditions such as medical emergencies or buying a house.
- Tax Benefits:
- Employee contributions to EPF are eligible for deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, up to ₹1.5 lakh per annum.
Compliance Requirements
- Registration:
- Employers with 20 or more employees must register with the EPFO.
- Monthly Contributions:
- Contributions must be deposited monthly within 15 days from the end of the month to which they relate.
- Filing Returns:
- Employers must file monthly returns (ECR) detailing employee contributions.
- Maintaining Records:
- Employers should maintain records of contributions, withdrawals, and any changes in employee status.
- Annual Returns:
- Annual returns need to be filed, including Form 3A (Annual Statement of EPF Contributions) and Form 6A (Annual Return of EPF).
- Compliance Audits:
- Regular audits may be conducted by the EPFO to ensure adherence to EPF regulations.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Penalties: Employers failing to comply with EPF regulations may face penalties, including fines and interest on delayed payments.
- Legal Action: Continuous non-compliance can lead to legal action against the employer.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to EPF regulations is crucial for both employers and employees. Compliance ensures that employees receive their entitled benefits while protecting employers from legal and financial repercussions. Organizations should implement robust payroll systems and maintain accurate records to facilitate compliance with EPF regulations.
“Fast-Track Your HR Career! Gain practical HR skills, a recognized certification, and career support at Next Innovation Asia. Your future in HR starts here—enroll today!”